Women reaches a higher population count than men
Based on the results of the 2020 Census of Population and Housing (CPH), the
City of Manila had a total population of 1,846,513. Through the period of 2015 to 2020, the number of citizens in the city had increased by 3.7 percent or by 66,365 persons. (See Table 1)
The total population is composed of household and institutional population. Within the total population of Manila in 2020, 1,837,785 were household and 8,728 were institutional. (See Table 1)
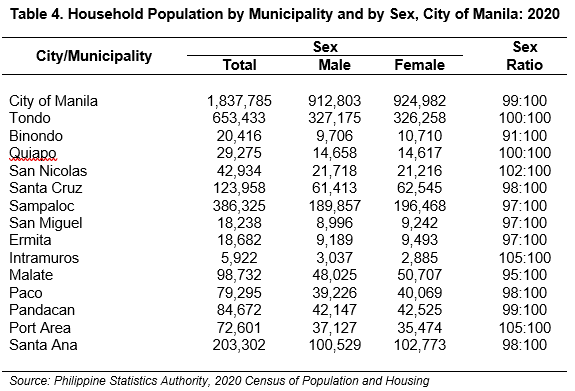
Meanwhile, in the number of household population, women (924,982) outnumbered men (912,803) by 0.6 percent or by 12,179 persons. With these figures, the sex ratio in 2020 resulted in 99 males for every 100 females. (See Table 4)
In comparison to 2015, women also outnumbered men but with a higher percentage rate than in 2020. Women exceeded the number of men by 1.8 percent or by 32,724 persons, resulting in a sex ratio of 96 males for every 100 females. (See Table 3)
Ermita holds the highest record for the growth rate of women and men in Manila
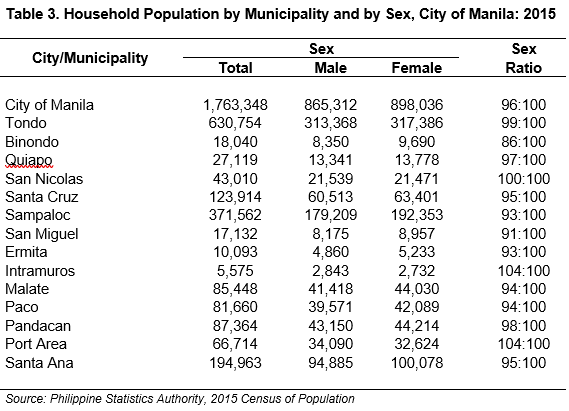
Among the 14 municipalities of Manila, Tondo had the highest number of women and men wherein Manileñas were 326,258 and Manileños were 327,175. Tondo also prevailed as the municipality with the highest population back in 2015 with 630,754 persons – 317,386 were women and 313,368 were men. (See Figure 1 and Table 3 and 4)

On the other hand, the municipality recorded with the lowest number of populations in 2015 and 2020 was Intramuros. The municipality had 2,732 women and 2,843 men in 2015 while 2,885 women and 3,037 men in 2020. Despite women dominating the household population, there are still municipalities where men had a higher population than women. (See Figure 1 and Table 3 and 4)
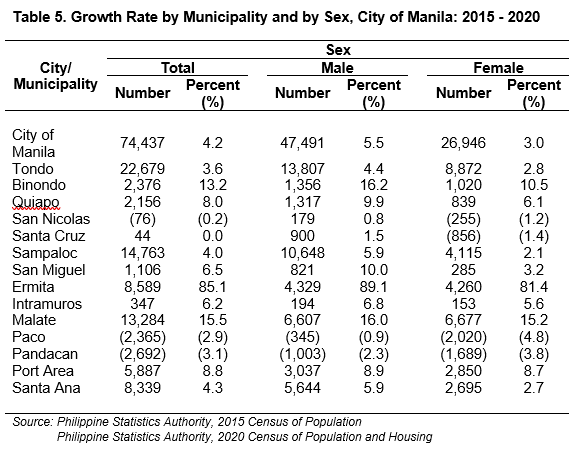
Moreover, regardless of Tondo having the highest number of women and men, the municipality of Ermita recorded the highest growth rate of women and men in 2020 at 81.4 percent and 89.1 percent, respectively. (See Table 5)
The number of Manileñas being declared as household head is gradually increasing
There was a total of 486,293 household heads in the city as of 01 May 2020. Seven (7) out of 10 of these household heads were men (336,664) while three (3) out of 10 were women (149,629). The household head is a person who is 15 years old and over who generally provides the chief source of income for the household unit. It is an adult person, male or female, who is responsible for the organization and care of the household or who is regarded as such by the members of the household. In comparison to 2015, the household heads increased by 11.7 percent or 51,056 persons in 2020. (See Table 6)
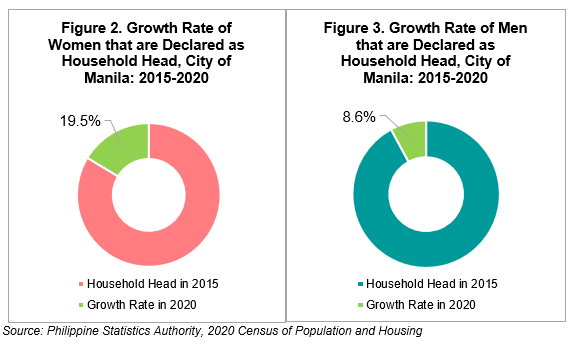
As time goes by, more males were consistently declared as the household head by their family or by their household members. However, we can also observe that the number of women who were declared as the household head were also gradually increasing. In fact, from 2015 to 2020, the number of women declared as the household head increased by 19.5 percent or by 24,442 persons. Meanwhile, household heads that were men increased by 8.6 percent or by 26,614 persons. (See Figure 2 and 3 and Table 6)
About 27.0 percent of the household population of Manila are married
In 2020, nearly half (49.1% or 902,945) of the household population of Manila were single wherein 430,308 were women and 472,637 were men. Moreover, about 27.0 percent (27.4% or 504,402) were married wherein 252,600 were women and 251,802 were men. Meanwhile, 43,078 were common-law or in a live-in set-up wherein 27,753 were women and 15,325 were men. On the other hand, roughly 4.0 percent (3.7% or 68,205) of the household population have been divorced, separated, or annulled wherein 54,397 were women and 13,808 were men. In addition, more than 300,000 (17.3% or 318,765) lost their wife or husband through death wherein 159,700 were women and 159,065 were men. However, there were 390 persons whose marital status was left unknown. (See Table 2)
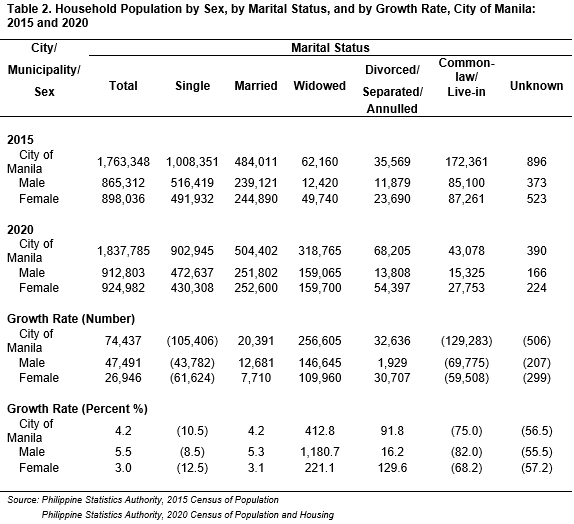
In contrast with 2015, the marital status of citizens in the city had a drastic change. The percentage of individuals who had a marital status of married, widowed, and divorced or separated raised by 4.2 percent (20,391), 412.8 percent (256,605), and 91.8 percent (32,636), respectively. On the contrary, the percentage of women and men who had a marital status of single, common-law or live-in, and unknown fell off by 10.5 percent, 75.0 percent, and 56.5 percent, respectively. (See Table 2)
The number of literate women in Manila is 1.2 percent higher than men
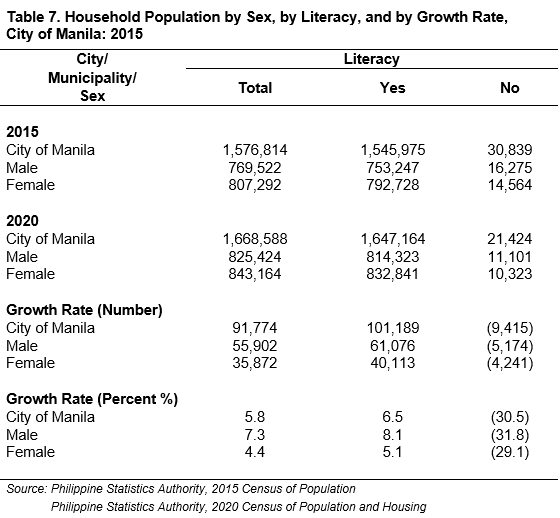
About 99.0 percent (98.7% or 1,647,164) of the residents in Manila ages 5 years old and over can read, write, and understand simple messages. Manileñas contributed approximately 51.0 percent (50.6% or 832,841) to this population, while Manileños contributed around 49.0 percent (49.4% or 814,323). (See Table 7)
The number of literate individuals in the city in 2020 were 6.5 percent (101,189) higher compared to the number of literate individuals in 2015. (See Table 7)

Figure 4 and 5 shows the growth rate of literate women and men in the City of Manila from the period of 2015 to 2020. The development rate of literate men were 3.0 percent (8.1% or 61,076) higher than women (5.1% or 40,113). (See Figure 4 and 5 and Table 7)

(SGD.) Amelia G. Basilio
Chief Statistical Specialist
Officer-in-Charge
